Acute flaccid myelitis
What is AFM?
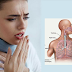
AFM is a rare disease that affects the spinal cord, the part of the nervous system that carries messages to and from the brain. Symptoms of AFM include sudden (acute) weakness in the arm(s) or leg(s), along with the loss of muscle tone and decreased or absent reflexes. Some people with AFM report pain. In some cases, AFM can affect the nerves controlling the head and neck, causing facial weakness, drooping of the eyelids, and difficulty swallowing, speaking, or moving the eyes. The most serious complication of AFM is a respiratory failure if the muscles involved with breathing become weakened. Most cases of AFM have been in children, but it can develop in adults.
Many times symptoms of AFM develop after a viral infection, such as poliovirus, West Nile virus, and adenovirus. In some cases, no clear possible cause is found. In addition, even when associated with a viral infection, it is not known how the infection triggers AFM, and it is not clear why some people develop AFM after an infection and others do not.
Prevention
To prevent infections by AFM-related viruses, specialists recommend staying up-to-date with polio vaccines and to minimize exposure to mosquitoes. There is no specific treatment for AFM. Treatments that have been tried include immunoglobulin, corticosteroids, plasma exchange, and antiviral therapy, but there is no clear evidence that any of these treatments affect recovery. Other treatment is supportive and depends on the symptoms. Physical therapy and occupation therapy are especially important during recovery. The extent of recovery varies. Although some people may make a full recovery, most have continued muscle weakness even after a year. Long-term outcomes are not known.source: NIH





No comments